Explore the AI4SoilHealth project’s YouTube channel to discover a series of videos focused on soil health monitoring. SMEG has contributed by producing content that highlights...
Read more...
Blog
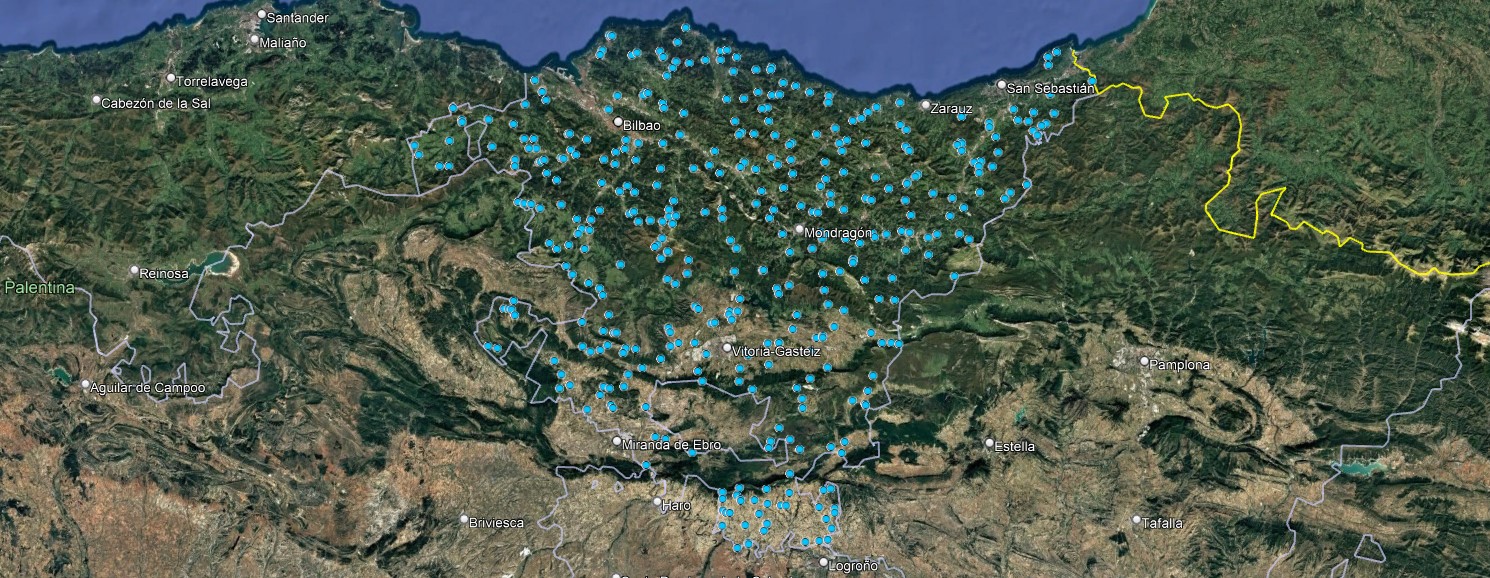
Basque soil health monitoring network (LURNET)
Through a collaboration with the OpenGeoHub Foundation, we have designed a soil health monitoring network for the Autonomous Community of the Basque Country. The sampling...
Read more...
Read more...
Vineyards network for co-creation and expansion of AgroEcological strategies to face viticulture challenges: a basis for cross-border living labs (VinAE; 2025-2028)
Agroecological practices (AE) in vineyards, such as the establishment of ground covers to protect soil from erosion and enhance its functionality, biodiversity, and associated ecosystem...
Read more...
Read more...
Documentary on antibiotic resistance
Our field experiment on the interactive effects of pesticide residues and Tº increase in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance in agroecosystems has appeared on the...
Read more...
Read more...
Biological remediation treatments improve the health of a mixed contaminated soil before significantly reducing contaminant levels
Authors: June Hidalgo, Unai Artetxe, José M. Becerril, María T. Gómez-Sagasti, Lur Epelde, Juan Vilela, Carlos Garbisu Journal: Environmental Science and Pollution Research DOI: 10.1007/s11356-023-31550-0 (more…)...
Read more...
Read more...
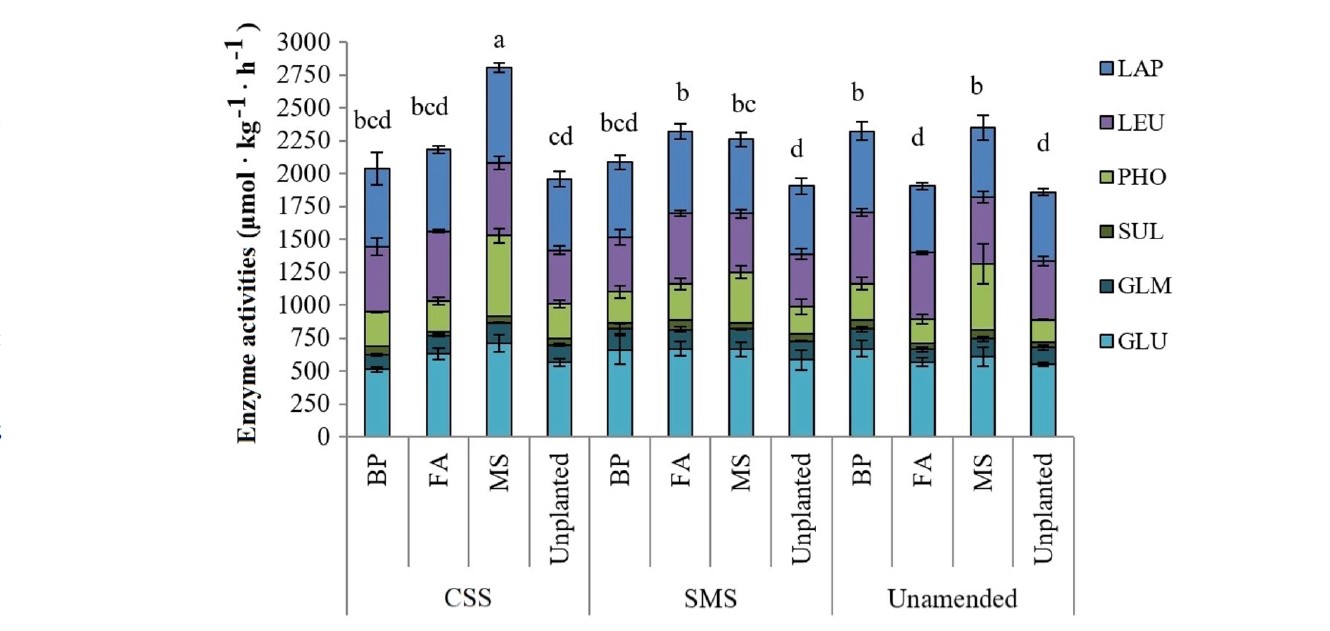
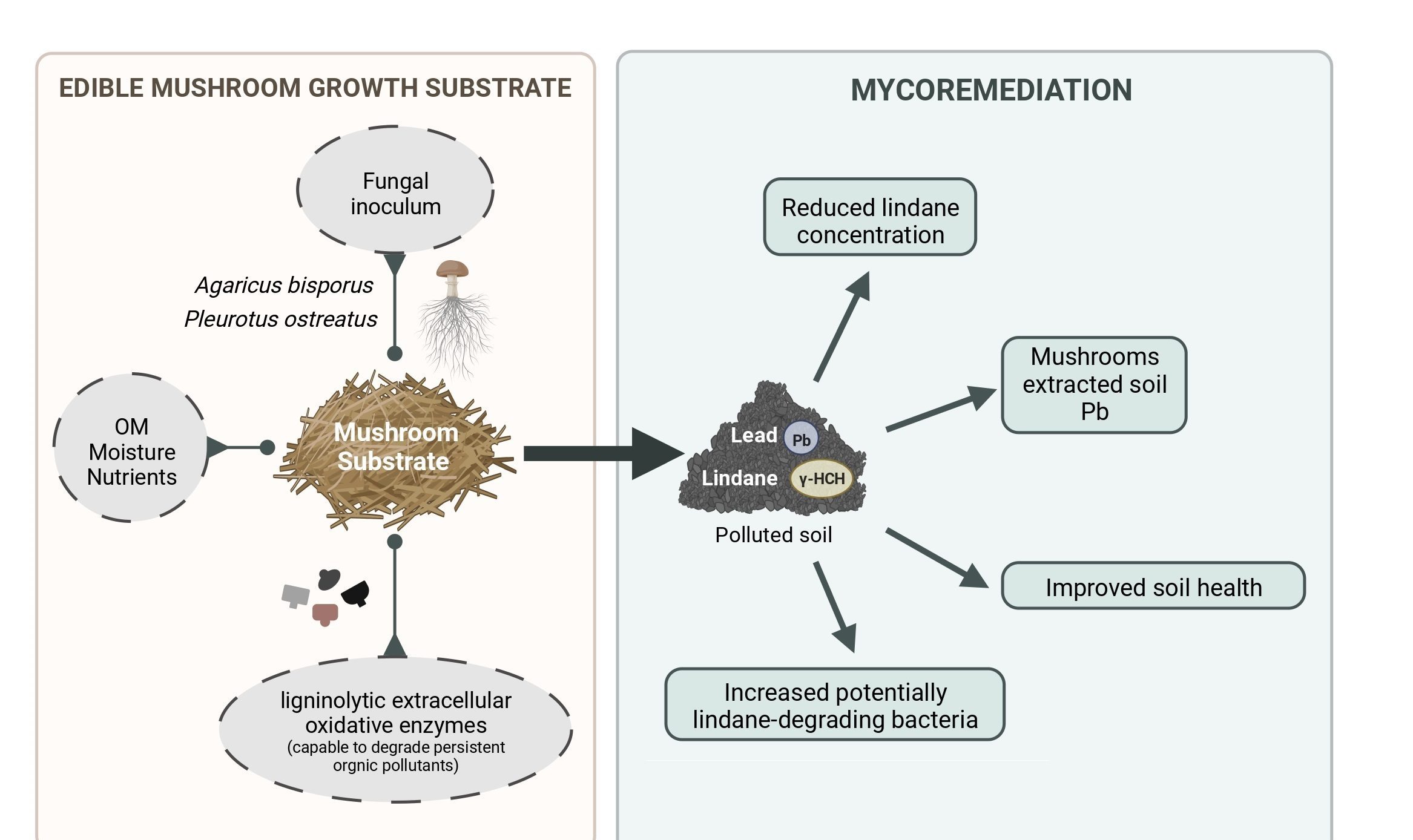
Mycoremediation with Agaricus bisporus and Pleurotus ostreatus growth substrates versus phytoremediation with Festuca rubra and Brassica sp. for the recovery of a Pb and γ-HCH contaminated soil
Authors: June Hidalgo, Lur Epelde, Mikel Anza, José M. Becerril, Carlos Garbisu Journal: Chemosphere https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138538 (more…)...
Read more...
Read more...
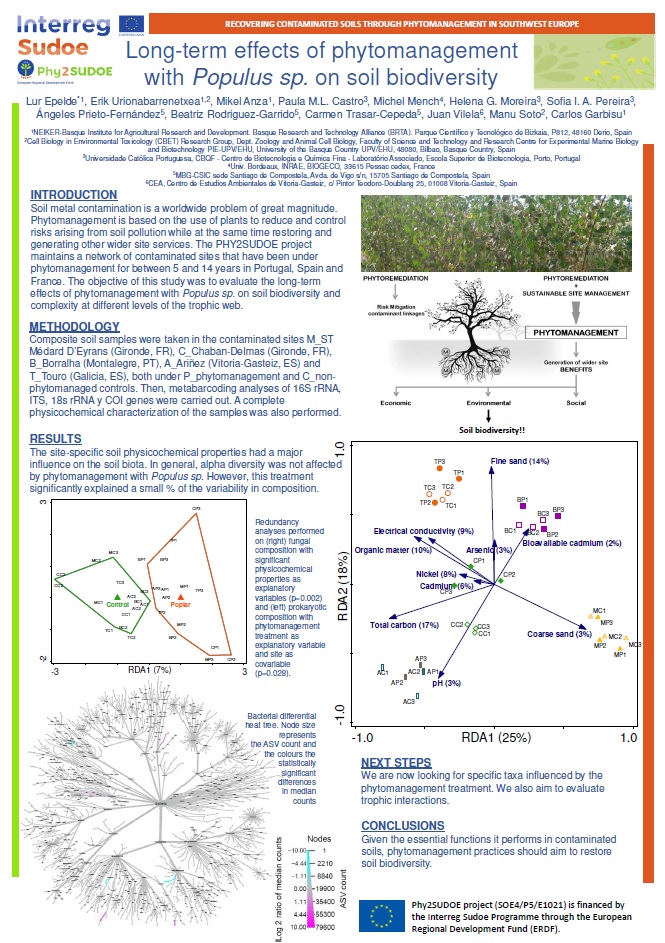
Communication at the 3rd Global Soil Biodiversity Conference
Soil metal contamination is a worldwide problem of great magnitude. Phytomanagement is based on the use of plants to reduce and control risks arising from...
Read more...
Read more...
Documentary on sustainable food production
We have taken part in the recording of a documentary on sustainable food production for the Teknopolis programme of ETB. We have explained the soil...
Read more...
Read more...
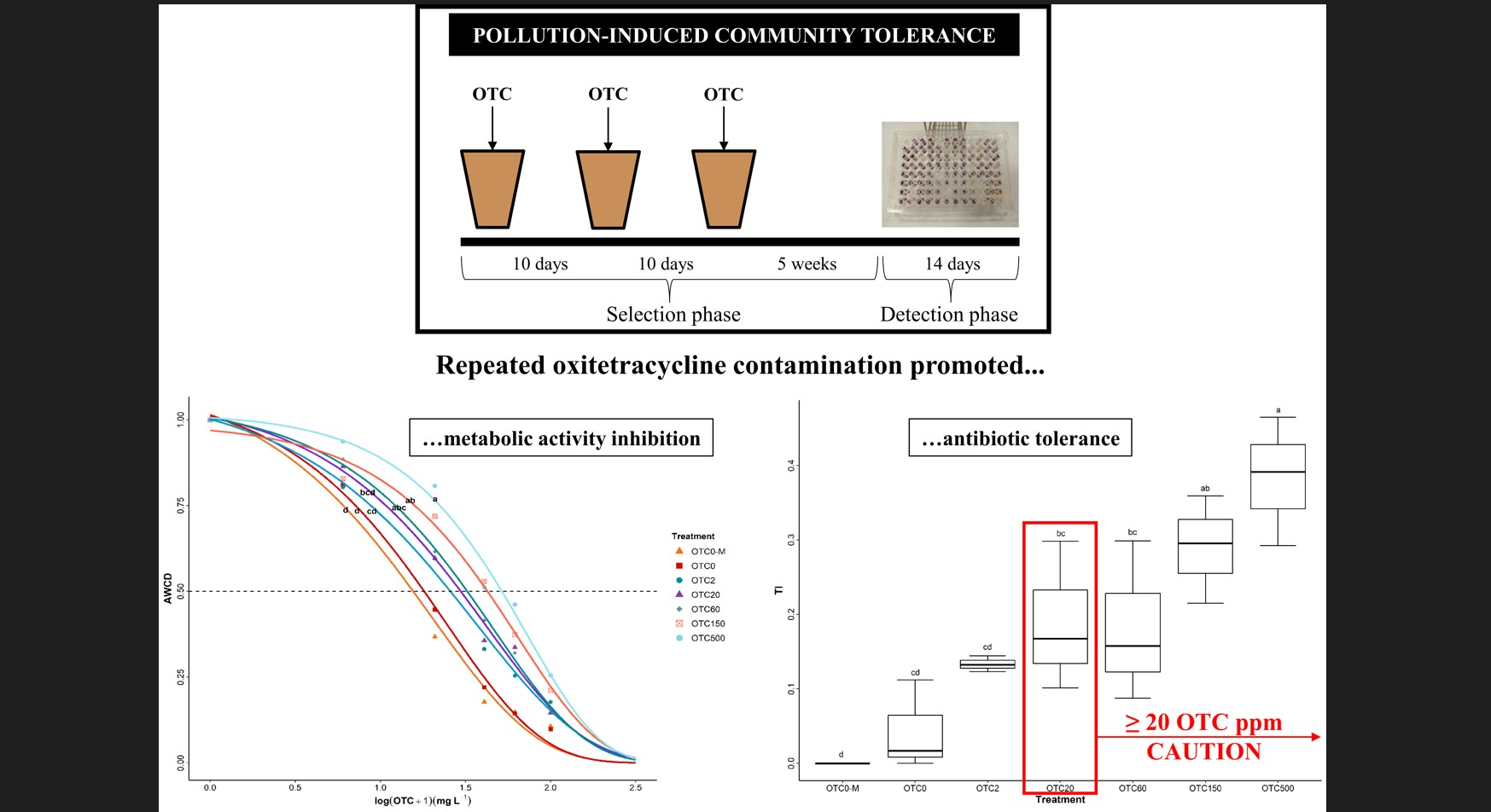
Induced development of oxytetracycline tolerance in bacterial communities from soil amended with well-aged cow manure
Authors: Leire Jauregi, Lur Epelde, Maddi Artamendi, Fernando Blanco, Carlos Garbisu Journal: Ecotoxicology https://rdcu.be/c9sNj (more…)...
Read more...
Read more...